Signal Divergence and Speciation at the Species Level

What processes drive signal divergence and what is the role of signal divergence in speciation? I investigated these questions by looking at geographic color variation of dewlaps (throatfans) in an Anolis lizard, Anolis distichus. I found that the repeated pattern of dewlap divergence across Hispaniola was correlated with environmental variation. Furthermore, using a common garden breeding experiment and experimental manipulation of dietary pigments, I found dewlap color and pattern to be highly heritable with no evidence of plastic change with dietary supplementation. Together, these results provide strong evidence that dewlap divergence is driven by adaptation to heterogeneous environments.
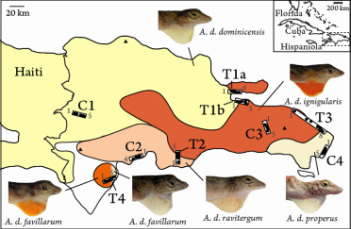
To assess whether adaptive dewlap color is associated with reproductive isolation, I examined contact zones between phenotypically divergent populations using a combination of phenotypic measurements, ecological data, and mitochondrial and nuclear genetic markers. I found that both ecological speciation and local adaptation of dewlaps, maintained in the face of neutral gene flow, contribute to dewlap color variation in A. distichus.
Associated publications:
Ng J., Geneva, A.J., Noll, S. and Glor R.E. 2017. Signals and speciation: Anolis dewlap color as a reproductive barrier. Journal of Herpetology. 51(3): 437-447
Ng J., Ossip-Klein A.G., Glor R.E. 2016. Adaptive signal coloration maintained in the face of gene flow in a Hispaniolan Anolis Lizard. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 16: 193
Ng. J., Kelly, A.L., MacGuigan, D.J. and Glor, R. E. 2013. The role of genetic and dietary factors in the sexual signal of a Hispaniolan Anolis lizard, Anolis distichus. Journal of Heredity. 104(6): 862-873
Ng, J., Landeen, E.L., Logsdon, R.M. and Glor, R.E. 2013. Correlation between Anolis lizard dewlap phenotype and environmental variation indicates adaptive divergence of a signal important to sexual selection and species recognition. Evolution. 67(2): 573-582
Ng, J. and Glor, R.E. 2011. Genetic differentiation among populations of a Hispaniolan trunk anole that exhibit geographic variation in dewlap color. Molecular Ecology. 20(20): 4302-4317
Ng, J. and Glor, R.E. 2010. Dewlap color variation and reproductive isolation in Anolis distichus. In: The Sixth Anolis Newsletter eds. Mahler, D.L., Herrel, A. and Losos, J.B., pp. 164-168. Museum of Comparative Zoology, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Ng, J., Perkins, S. L., Dussmann, E. J. and Glor, R.E. 2009. Eleven highly polymorphic microsatellite markers for the lizard Anolis distichus. Conservation Genetics Resources. 1(1): 135-139
Ng J., Geneva, A.J., Noll, S. and Glor R.E. 2017. Signals and speciation: Anolis dewlap color as a reproductive barrier. Journal of Herpetology. 51(3): 437-447
Ng J., Ossip-Klein A.G., Glor R.E. 2016. Adaptive signal coloration maintained in the face of gene flow in a Hispaniolan Anolis Lizard. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 16: 193
Ng. J., Kelly, A.L., MacGuigan, D.J. and Glor, R. E. 2013. The role of genetic and dietary factors in the sexual signal of a Hispaniolan Anolis lizard, Anolis distichus. Journal of Heredity. 104(6): 862-873
Ng, J., Landeen, E.L., Logsdon, R.M. and Glor, R.E. 2013. Correlation between Anolis lizard dewlap phenotype and environmental variation indicates adaptive divergence of a signal important to sexual selection and species recognition. Evolution. 67(2): 573-582
Ng, J. and Glor, R.E. 2011. Genetic differentiation among populations of a Hispaniolan trunk anole that exhibit geographic variation in dewlap color. Molecular Ecology. 20(20): 4302-4317
Ng, J. and Glor, R.E. 2010. Dewlap color variation and reproductive isolation in Anolis distichus. In: The Sixth Anolis Newsletter eds. Mahler, D.L., Herrel, A. and Losos, J.B., pp. 164-168. Museum of Comparative Zoology, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Ng, J., Perkins, S. L., Dussmann, E. J. and Glor, R.E. 2009. Eleven highly polymorphic microsatellite markers for the lizard Anolis distichus. Conservation Genetics Resources. 1(1): 135-139
